Affiliate Disclaimer:
Some of the links on this website are affiliate links, which means that if you click on a link and make a purchase, we may earn a commission at no extra cost to you. This helps support the website and allows us to continue creating content. We only recommend products or services we personally use or genuinely believe will add value to our readers.
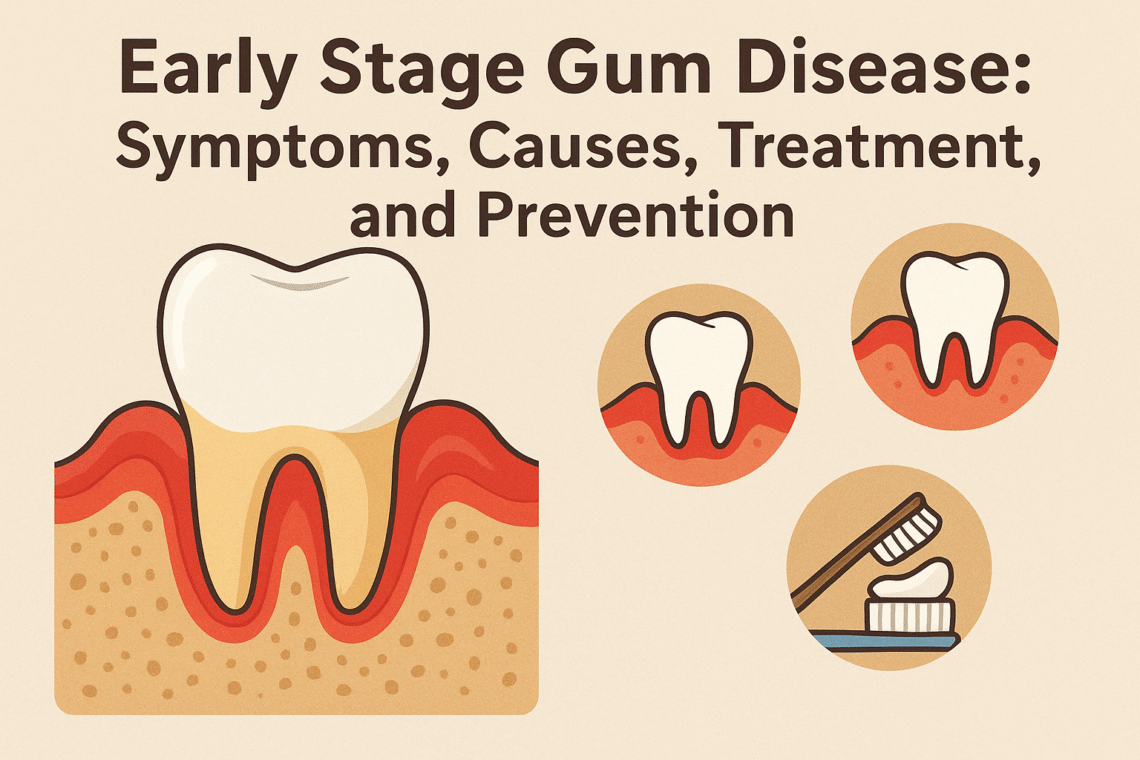
Gum health is a critical component of overall oral hygiene, yet it often receives less attention than it deserves. Early stage gum disease, also known as gingivitis, is one of the most common yet overlooked dental problems worldwide. If left untreated, it can progress to more severe forms of gum disease such as periodontitis, which can result in tooth loss and systemic health issues. Understanding what early stage gum disease is, how it develops, and the steps you can take to prevent and treat it is essential for maintaining long-term oral health.
What is Early Stage Gum Disease?
Early stage gum disease, or gingivitis, is the initial phase of gum inflammation caused primarily by plaque buildup along the gumline. Plaque is a sticky film of bacteria that forms on teeth after eating and drinking. If plaque is not removed through regular brushing and flossing, it hardens into tartar, which irritates the gums and triggers inflammation.
Unlike advanced gum disease, early stage gum disease does not usually cause pain, making it easy to ignore. However, the symptoms, though mild, can be noticeable and should never be overlooked. Gingivitis is reversible if caught early, but neglecting it can lead to permanent damage.
Symptoms of Early Stage Gum Disease
The first signs of gingivitis are often subtle, but they serve as important warnings. Common symptoms include:
- Red or swollen gums: Healthy gums should appear firm and pink. Swelling and redness are signs of irritation and inflammation.
- Bleeding gums: Bleeding while brushing, flossing, or eating hard foods is one of the most common symptoms of early gum disease.
- Bad breath (halitosis): Bacterial buildup in the mouth can produce unpleasant odors.
- Tenderness in gums: Gums may feel sore or sensitive when touched.
- Receding gums: In some cases, gums may start to pull away from teeth, creating pockets where bacteria can thrive.
Recognizing these symptoms early is critical because gingivitis can be reversed with proper care, unlike periodontitis, which involves permanent damage to gums and bone.
Causes of Early Stage Gum Disease
Several factors contribute to the onset of early stage gum disease. The primary cause is plaque accumulation, but other risk factors can accelerate or worsen the condition.
- Poor Oral Hygiene
Infrequent or improper brushing and flossing allow plaque to build up on teeth and gums, triggering inflammation. - Smoking and Tobacco Use
Tobacco weakens the immune system, making it harder for gums to heal and fight infections. Smokers are at a much higher risk of developing gum disease. - Hormonal Changes
Pregnancy, puberty, and menopause can make gums more sensitive, increasing susceptibility to gingivitis. - Medical Conditions
Diseases such as diabetes, HIV/AIDS, and cancer can compromise the immune system and make gums more prone to infection. - Medications
Certain drugs reduce saliva flow, causing dry mouth. Since saliva helps wash away bacteria, reduced saliva increases gum disease risk. - Poor Nutrition
A diet lacking in essential nutrients, especially vitamin C, can impair gum health. - Genetics
Some individuals may be genetically predisposed to gum problems, making prevention even more important.
The Stages of Gum Disease Progression
Understanding the progression of gum disease helps highlight why early intervention is so crucial.
- Gingivitis (Early Stage Gum Disease)
Symptoms include gum inflammation, redness, and bleeding. At this stage, there is no damage to bone or connective tissue. - Mild Periodontitis
If untreated, gingivitis progresses to periodontitis, where the inner layer of the gum pulls away from teeth, forming small pockets that trap food and bacteria. - Moderate to Severe Periodontitis
Infection spreads deeper into the bone and supporting structures of the teeth. This can result in loosening of teeth, gum recession, and bone loss. - Advanced Periodontitis
Teeth may shift, loosen, or fall out due to extensive damage to bone and connective tissues.
Catching gum disease in the early stage is key, since it is reversible at that point.
How to Diagnose Early Stage Gum Disease
Early stage gum disease is typically diagnosed during a dental check-up. Dentists and hygienists will:
- Examine gums for swelling, redness, and bleeding.
- Measure pocket depth between teeth and gums using a periodontal probe.
- Assess tartar buildup along the gumline.
- Review medical history and lifestyle factors that may contribute to gum health issues.
Regular dental visits (at least twice per year) are crucial because professionals can identify gum disease before symptoms become severe.
Treatment for Early Stage Gum Disease
The good news is that gingivitis is reversible with timely treatment. Common treatment methods include:
- Professional Dental Cleaning
Dentists or hygienists perform scaling and polishing to remove plaque and tartar buildup. Deep cleaning may be necessary in some cases. - Improved Oral Hygiene at Home
- Brush at least twice a day using a soft-bristled toothbrush.
- Floss daily to remove food particles and plaque between teeth.
- Use an antimicrobial or fluoride mouthwash to reduce bacteria.
- Lifestyle Changes
- Quit smoking and avoid tobacco use.
- Maintain a balanced diet rich in vitamins and minerals.
- Stay hydrated to promote saliva flow.
- Regular Dental Visits
Ongoing monitoring helps ensure gums remain healthy and prevents progression.
With consistent oral hygiene and professional care, early stage gum disease can be completely reversed.
Home Remedies for Early Stage Gum Disease
While professional treatment is essential, some home remedies can complement oral care:
- Saltwater Rinse: Gargling with warm saltwater helps reduce inflammation and kill bacteria.
- Green Tea: Contains antioxidants that promote gum health.
- Aloe Vera Gel: Applying aloe vera gel to gums can reduce swelling and irritation.
- Oil Pulling: Swishing coconut or sesame oil in the mouth may help reduce bacteria.
These remedies should not replace dental visits but can provide additional support.
How to Prevent Early Stage Gum Disease
Prevention is always better than cure. The following steps can help protect against early gum disease:
- Brush Correctly and Consistently
Use proper brushing techniques and replace toothbrushes every 3–4 months. - Floss Daily
Flossing removes plaque and food particles that brushing alone cannot reach. - Use Mouthwash
An antimicrobial mouth rinse reduces bacteria and freshens breath. - Regular Dental Visits
Professional cleanings prevent tartar buildup and allow early detection of issues. - Balanced Diet
Eat plenty of fruits, vegetables, and foods rich in vitamin C and calcium. - Avoid Tobacco
Smoking is one of the most significant risk factors for gum disease. - Stay Hydrated
Drinking water helps wash away bacteria and keeps the mouth moist.
The Link Between Early Stage Gum Disease and Overall Health
Recent research suggests that gum health is closely tied to overall systemic health. Poor gum health has been linked to:
- Heart disease: Inflammation from gum disease may contribute to cardiovascular issues.
- Diabetes: Gum disease can worsen blood sugar control.
- Respiratory infections: Bacteria from the mouth can travel to the lungs.
- Pregnancy complications: Gum disease has been associated with premature birth and low birth weight.
Taking care of your gums does more than just protect your smile; it supports your overall well-being.
When to See a Dentist
If you notice symptoms such as persistent bad breath, bleeding gums, swelling, or gum tenderness, it’s important to schedule a dental appointment. Early intervention prevents long-term damage and ensures treatment remains simple and effective.
Final Thoughts
Early stage gum disease, or gingivitis, is extremely common but highly preventable and reversible. The key lies in maintaining proper oral hygiene, visiting your dentist regularly, and adopting healthy lifestyle habits. Ignoring the warning signs of gum disease can lead to severe oral health problems and even affect your overall health. By acting early, you can protect your teeth, gums, and smile for years to come.
If you suspect you may have early stage gum disease, don’t wait—schedule a dental check-up today and take the first step toward healthier gums and a brighter smile.